Legal framework
The legal framework for
the conservation of natural habitats and species in the Mediterranean
is provided
by the Convention for the Protection of the Mediterranean Sea against
Pollution (Barcelona Convention) (1976). The partecipanting countries agreed these
general obligations:
1.Take the necessary measures to:
(a) protect, preserve and manage in a
sustainable way areas of particular natural or cultural value, notably
by the establishment of specially protected areas;
(b) protect, preserve and manage threatened
or endangered species of flora and fauna.
2. Cooperate, directly or through the
competent international organizations, in the conservation and sustainable
use of biological diversity in the Mediterranean area .
3. Identify and compile inventories of
the components of biological diversity important for its conservation
and sustainable use.
4. Adopt strategies, plans and programmes
for the conservation of biological diversity and the sustainable
use of marine and coastal biological resources.
5. Identify processes and activities which
have or are likely to have a significant adverse impact on the conservation
and sustainable use of biological diversity, and monitor their effects.
Internationally protected areas
There are 122
specially protected area sites in the Mediterranean, but only Italy
has a specific legislation
about this matter. Other
countries don't have detailed rules concerning regulation and
management of their marine protected areas.
An agreement has been signed by
France, Italy and the Principality of Monaco for the creation of an
international sanctuary for Mediterranean cetaceans in the sea close
to these countries to protect cetaceans against direct catch and
other threats.
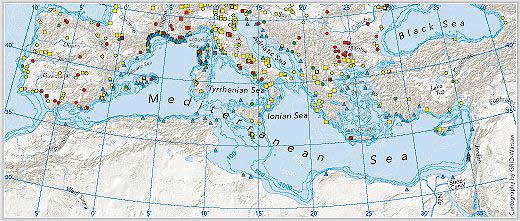
Specially
protected areas in the Mediterranean Sea of the Barcelona Convention
Source: UNEP-RAC/SPA,
1997b
Red List
There is no Red
List of Mediterranean marine fauna and flora. A draft list of endangered
or threatened
species was written under the Barcelona Convention. Non-governmental
organisations, with support from the national environmental agencies,
are involved in the protection of some of the most highly threatened
species. However, many of the rare species
of the Specially Protected Areas List, especially those of commercial
interest, are not adequately protected.
From European
Environment Agency
Environmental organizations in Italy
Italia nostra
National association on protection of historical, artistic and natural
resources.
Europa nostra
It’s aims include struggle against pollution and nature protection.
WWF Italia
Italian
section of WWF (WORLD WILDLIFE FOUND), was founded in 1966. the functions
organization carries out are:
- supervision
of protected territories
- protection
of endangered species (for example, seal, wolf, marine turtle)
- informs
the magistrates about all the norms violations
-
leads national
campaigns against pollution
Legambiente
Founded in 1979, fights for reasonable use of natural resources.
Organization has practically the same
task as WWF, particularly engages in environmental
education. LIPU
League founded in 1966. It is involved in birds’ protection.
Amici
della terra.
Organization founded in 1977 in connection with foundation of “Friends
of Earth”, recognized by UN.
LAC
Struggles for abolition of hunting.
LAN
National league founded in 1977. it struggles for prohibition of cruel
use of animals in experiment laboratories.
LIDA
Founded in 1977, fights for animals rights.
Federazione italiana pro natura
The oldest Italian association on nature protection.
Greenpeace
International organization, focuses on threats to biodiversity, has
presence in Italy. National
Parks, state and regional reserves
Taking into consideration National Parks, state and regional reserves,
it can be said that 10 % of Italian territory is protected. There
are :
- 21 National
Parks
- 143 natural
reserves of the state
- 16 marine
reserves
- 110 regional
National parks
- 252 regional
natural reserves
- 128 other
protected areas.
|

